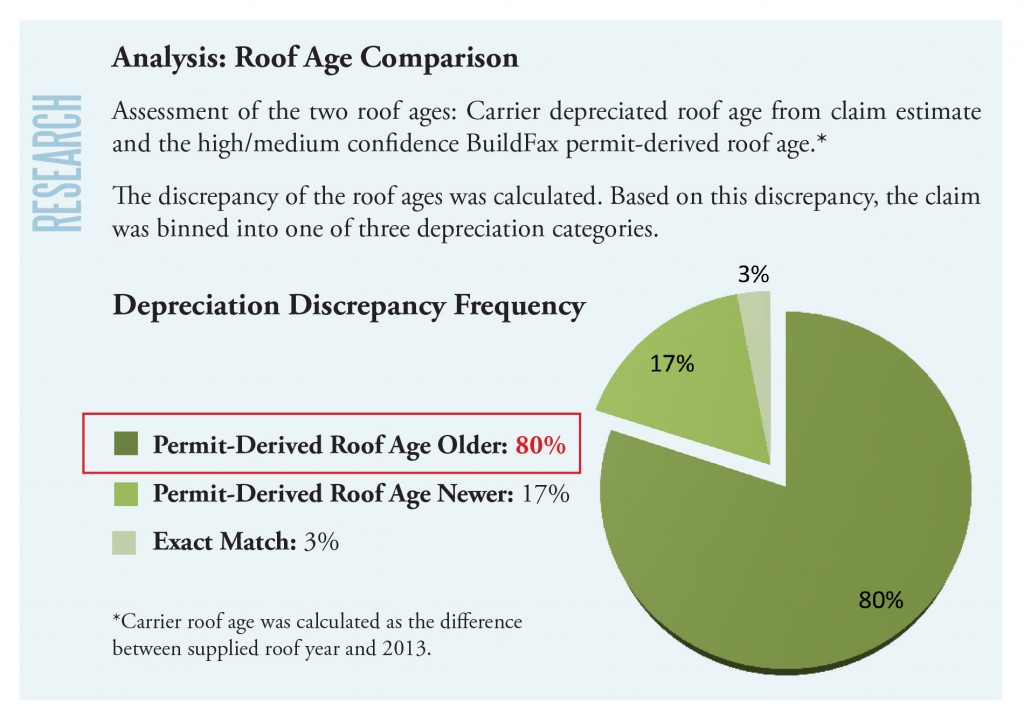
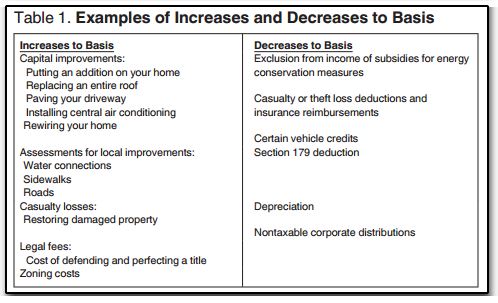
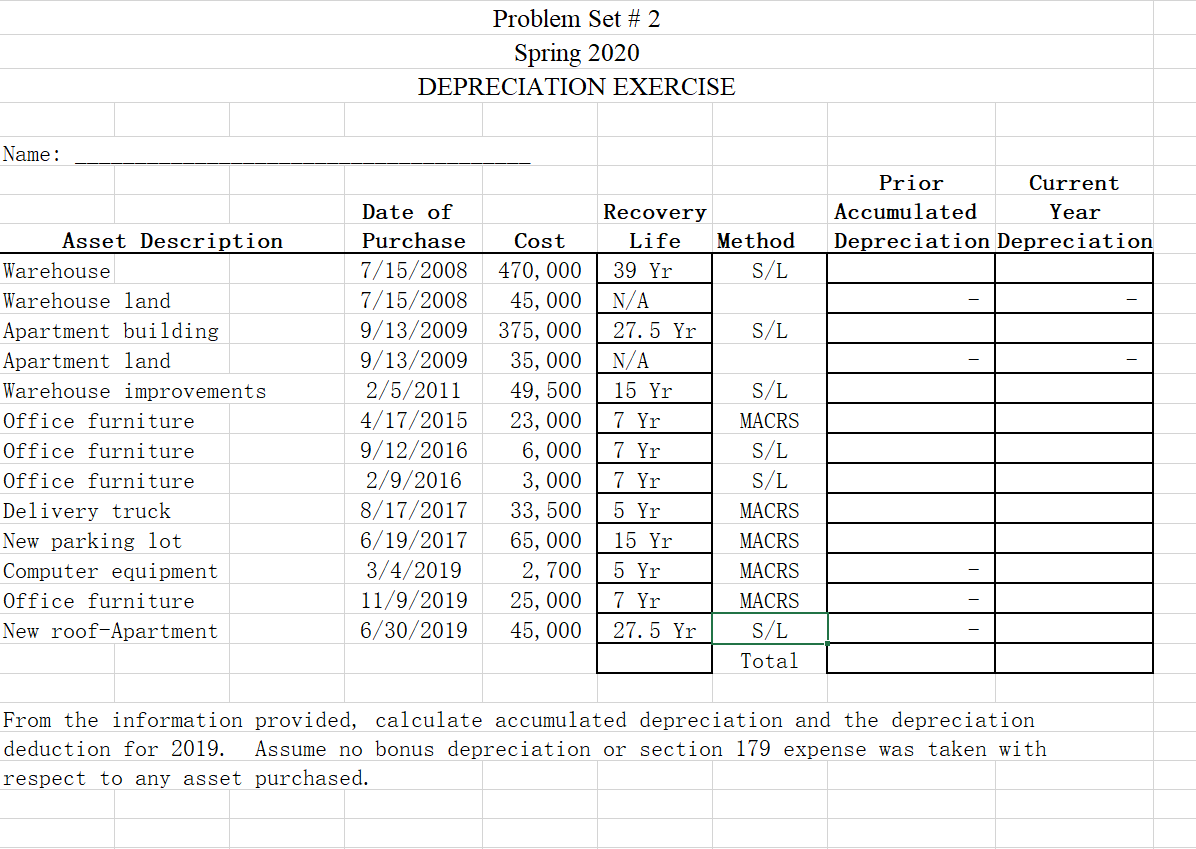
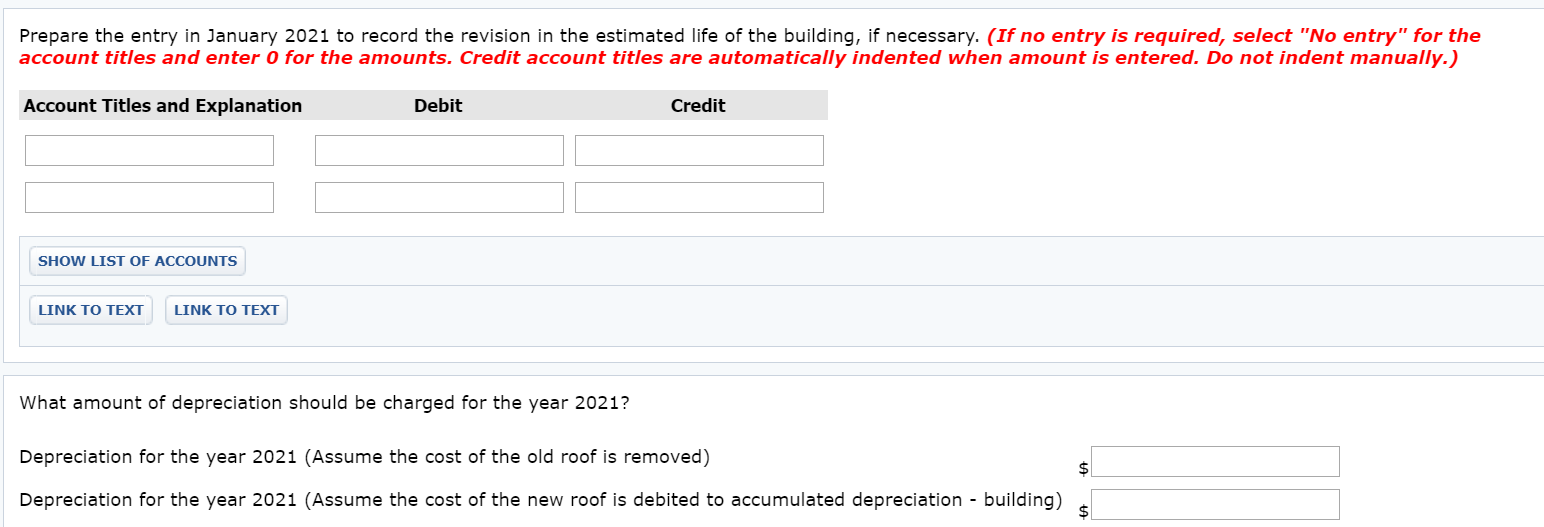
Roof Depreciation Life

A capital improvement is any major replacement or renovation that betters the rental property or.
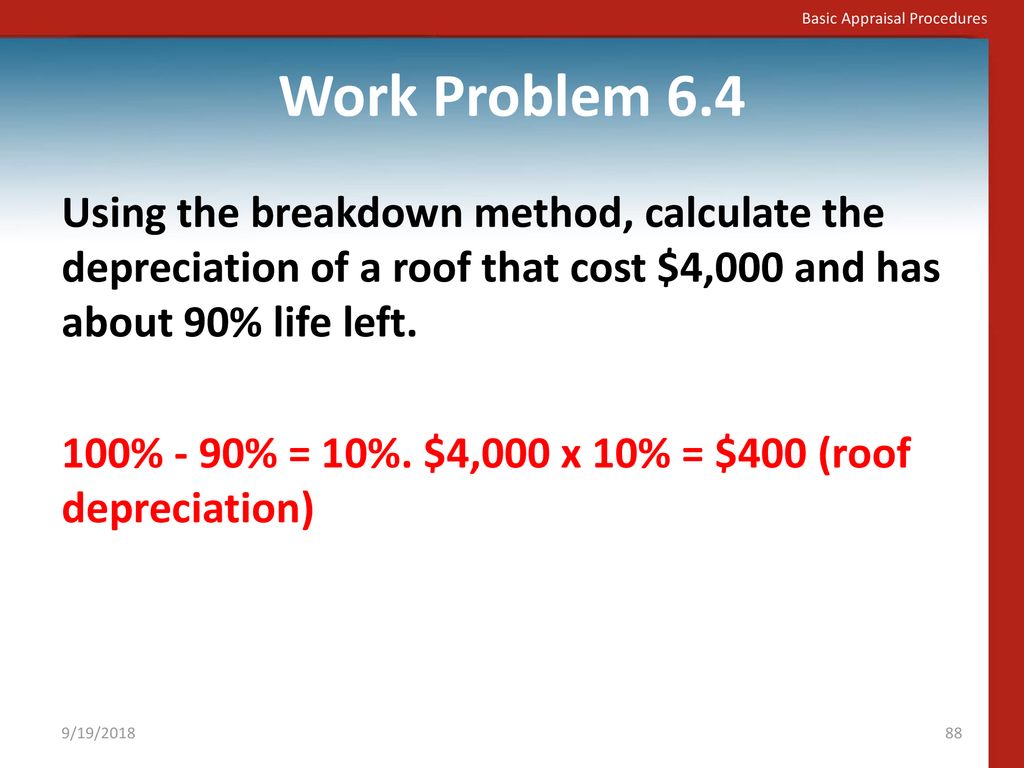
Roof depreciation life. Are generally depreciated over a recovery period of 27 5 years using the straight line method of depreciation and a mid month convention as residential rental property. For example if you ve owned a rental property for 10 years before you installed a new roof you can depreciate the roof over 27 5 years even though you have 17 years of depreciation left on the property. The most common and often significant item that is evaluated is roofing related work. The roof depreciates in value 5 for every year or 25 in this case.
How is depreciation on a roof calculated. For example if the new roof costs 15 000 divide that figure by 27 5. Changes to depreciation limitations on luxury automobiles and personal use property. If the taxpayer doesn t claim bonus depreciation the greatest allowable depreciation deduction is.
For example going from asphalt shingles 20 year life to clay tile 50 year life is a betterment that requires capitalization. This means the roof depreciates 545 46 every year. When a claims adjuster looks at a roof he will consider the condition of the roof as well as its age. How to depreciate a new roof on rental property.
Decide if the new roof is a capital improvement. The irs states that a new roof will depreciate over the course of 27 5 years for residential buildings and over the course of 39 years for commercial buildings. Figure out the beginning and end dates. Let s say your roof is supposed to last 20 years and it s 5 years old when damaged.
The irs uses the straight line method to calculate the depreciation of your roof which means that the depreciation of your roof is calculated evenly across a set period of time. In many cases only a portion of the roofing system is replaced and depending on the facts those costs may be deducted as repairs. Repainting the exterior of your residential rental property. If improved materials were used taxpayers would need to focus on the expected life of the old roof versus the expected life of the new roof.
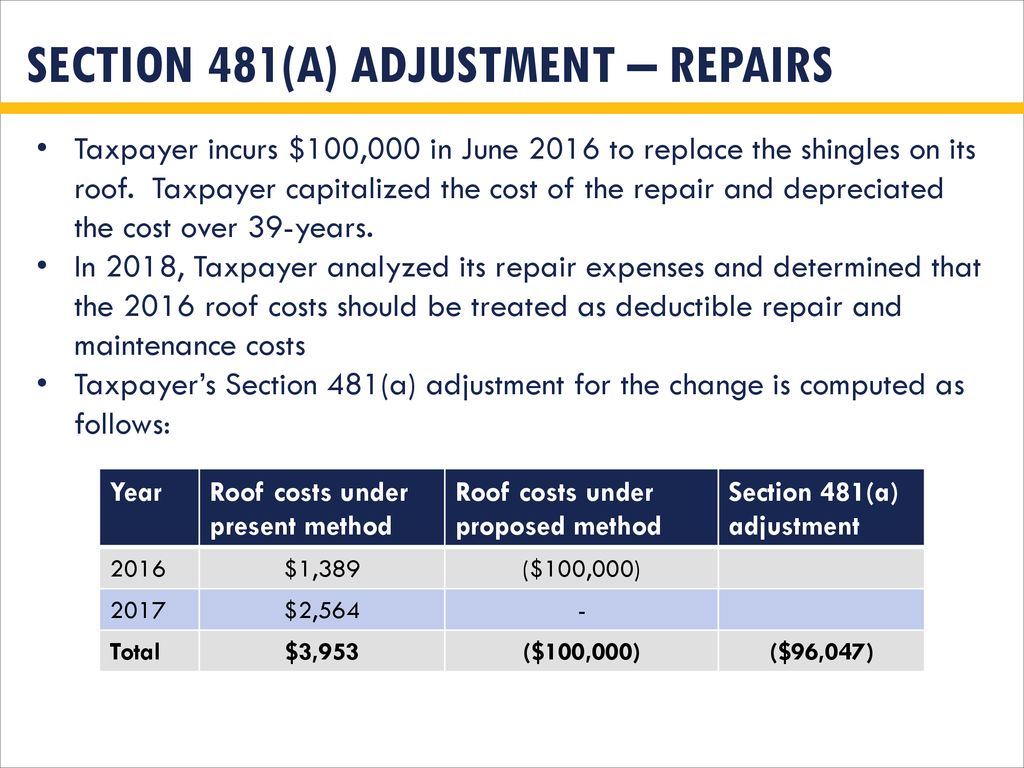
Each year tax professionals who deal with real estate must evaluate the most recent building expenditures and determine which items should be written off as a repair expense or capitalized.